Project
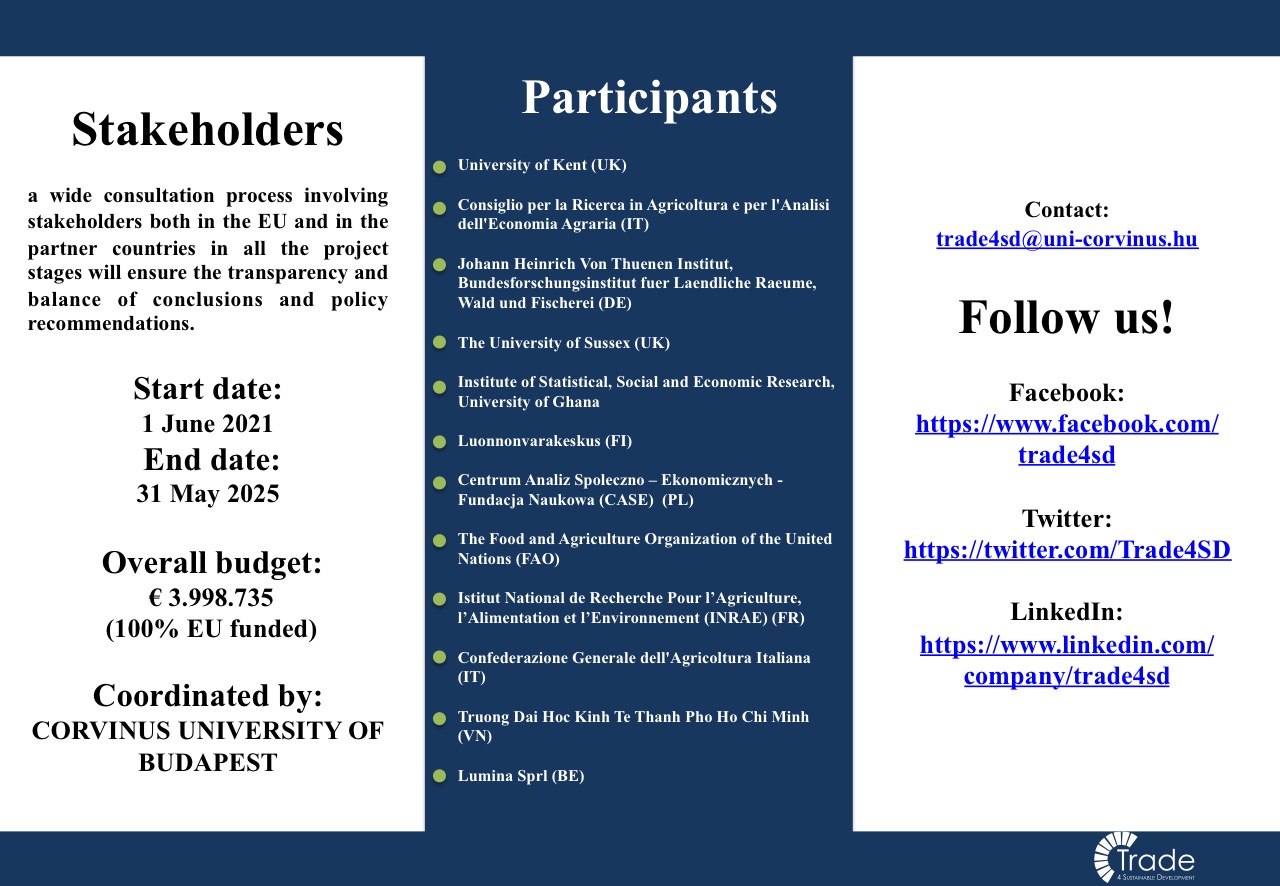
Trade4SD is a 4-year project devoted to research on a topic which is high on the domestic as well as multilateral, EU and bilateral trade policy agenda. The ambition of the project is to explore and foster the positive linkages between trade and sustainable development is to provide policy recommendations for the creation of new opportunities for agents involved in the global, regional and national agri-food value chains, and to define conditions for sustainable livelihoods of farm producers in the EU and developing partner countries. Trade is a central factor in shaping global, regional and local development. Increased trade, empowered by the growth of Global Value Chains (GVCs), has boosted productivity and incomes in many countries.
Trade can also contribute to food security, improved nutrition through diversification of food baskets and give poor farmers access to high value markets. However, if not fairly regulated, trade might generate increases in inequality and negative impacts on working conditions in developing countries, and compromise the environment. According to the recent World Bank Report (2020a), beyond policies to facilitate participation in Global Value Chains directly, complementary policies, such as labour regulations and environmental protection measures, are needed to share their benefits and attenuate any costs. Trade policy has an important part to play in achieving the SDGs.
Work Packages
-
WP1
Structured review on the relationships between international agricultural trade and sustainability
-
WP3
Quantitative model-based analysis of the sustainability impacts of agricultural trade
-
WP5
Coherence analysis of EU policy frameworks
-
WP7
Civil society dialogue, Communication, Dissemination and Exploitation
-
WP9
Ethics requirements
-
WP2
The role of WTO, and EU bilateral and regional trade agreement to meet SDGs: gaps and best practices
-
WP4
Qualitative in-depth analysis of linkages and case studies
-
WP6
Implications for policy
-
WP8
Coordination and project management